Pure Electronics
 ←Index
←Index
Integrated Circuits
by Professor Petabyte
Introduction
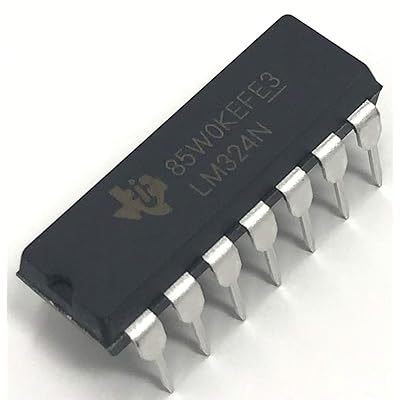
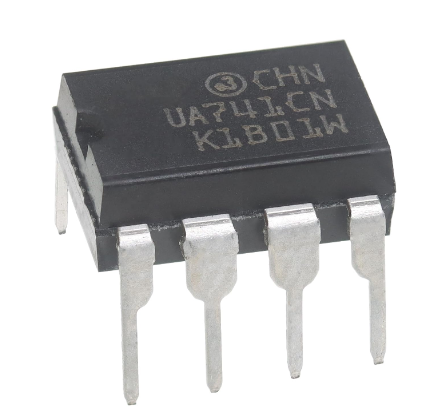
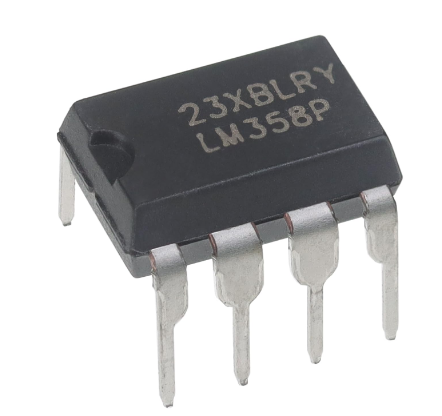
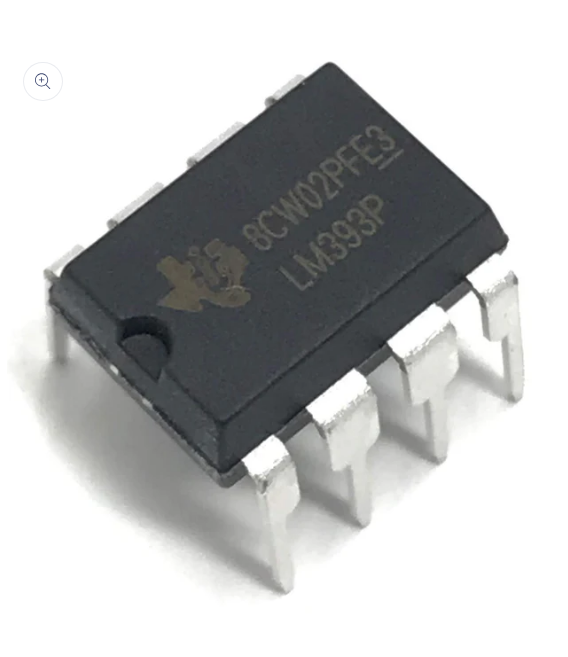
Inegrated Circuits are what most people are referring to when they say "Microchips". They are typically (although not neccessarily) black rectangular components with metal pins protruding from both side, like those in the picture.
Integrated Circuits are so called because they typically contain several miniturised components with apprpriate connections between those components, and also to the pins along each side of the IC. It would be possible to use full sized components to replicate the functionality of the IC, but that is the point of ICs - to provide little short-cuts, miniaturisation and convenience to device building. Very often a data sheet will include a circuit diagram of the components inside the IC as part of the explanation of how it works.
ICs with very large numbers of internal components include microprocessors, microcontrollers, FPGAs (Field-Programmable Gate Array), and memory chips. These components are typically found in computers, smartphones, and other complex electronic devices.
Microprocessors and Microcontrollers:
These ICs are the brains of many electronic devices, responsible for processing data and controlling operations. They can contain billions of transistors, allowing them to perform complex tasks.
FPGAs (Field-Programmable Gate Arrays):
These are programmable ICs that can be configured to perform various functions after manufacturing. They are often used in applications where custom hardware is needed, such as in aerospace and AI.
Memory ICs (RAM, ROM, Flash):
These ICs are used for storing data, both temporarily and permanently. They can also contain millions or even billions of transistors, allowing them to store large amounts of information.
Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs):
These are custom-designed ICs for specific applications, such as cellphones. They can incorporate both analog and digital functions, including sensor interfaces and memory
Standard ICs
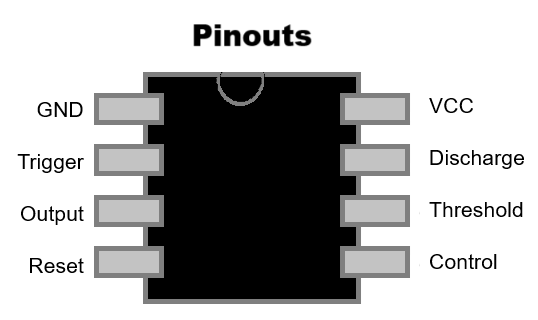
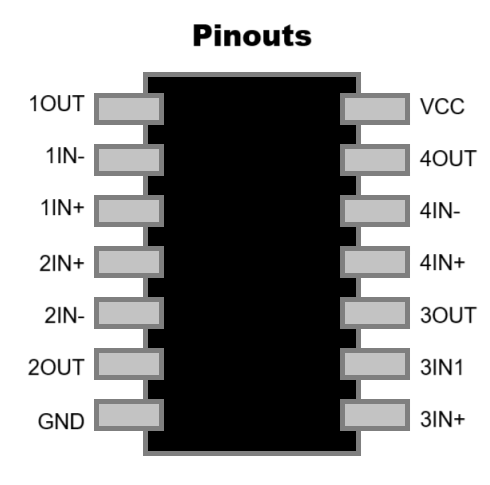
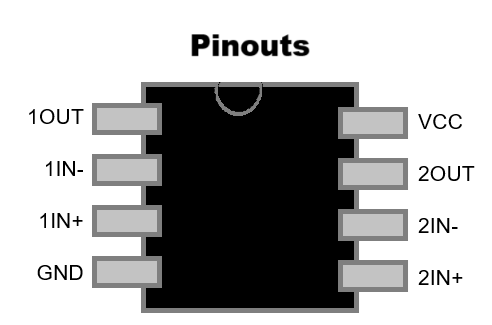
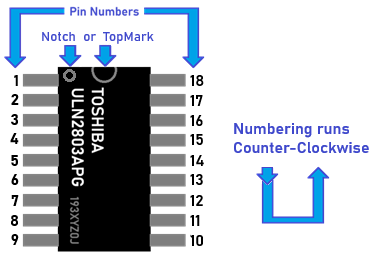 There are many types of standard ICs, each type serves a particular purpose. They most (but not all) have a similar general layout. At one end is a mark or indentation that indicated where the 'top' of the IC is, and the pins are numbered anticlockwise from that point. Where the indicator is not a central notch, it usuallu is closest to pin 1 of the IC. The type of IC, and sometimes (not always) the name of the manufacturer is printed on the IC.
There are many types of standard ICs, each type serves a particular purpose. They most (but not all) have a similar general layout. At one end is a mark or indentation that indicated where the 'top' of the IC is, and the pins are numbered anticlockwise from that point. Where the indicator is not a central notch, it usuallu is closest to pin 1 of the IC. The type of IC, and sometimes (not always) the name of the manufacturer is printed on the IC.
It is important to know where the top of the IC is to determine which pin is which. If the IC were inserted upside down for example, pin 1 would become pin 18, pin 2 would become pin 17, and so on. Sometimes the top mark is a cut-out or notch in the plastic, but it can just be a dot painted on.
Where an IC is mounted on a breadboard it is important that the IC straddles the center line, otherwise pins would be connected which should not be.
The IC manufacturers usually publish a "Data Sheet" for eacxh of their products, which explains operation, capabilities and tolerances etc.
Where possible for each of the ICs listed below there is a link to data sheet. Data sheets are neccessarily very technical documents, often detailed and quite lengthy, but they do hold the information vitel to understanding the IC and how to integrate it into a a working system.
IC Suffixes
The suffixes like 'N', 'P', 'D', etc., on IC part numbers (e.g., LM324N, LM358P) usually indicate the package type or manufacturer-specific info, not changes in electrical function. Here's a breakdown:
Common IC Suffixes and Their Meanings
| Suffix | Meaning | Example | Notes |
|---|
| N | DIP (Dual In-line Package) | LM324N | Through-hole package, easy for breadboarding. |
| P | Often also DIP (depends on maker) | LM358P | Used by some manufacturers like Texas Instruments. |
| D | SOIC (Small Outline IC) | LM358D | Surface-mount package for compact designs. |
| T | SOT-23 or similar small package | TLV2372T | Ultra-small surface mount. |
| R | TSSOP or SSOP package | LM324DR | Thin surface-mount variant. |
| A/B | Grade or temp range | LM324A | 'A' often means higher precision or range. |
| M | Military or extended temperature | LM358AM | Used in harsher environments. |
Manufacturer-Specific Differences
Some suffixes are branding conventions:
- TI uses 'P' for PDIP, 'D' for SOIC, etc.
- STMicroelectronics and others might use 'N' for DIP.
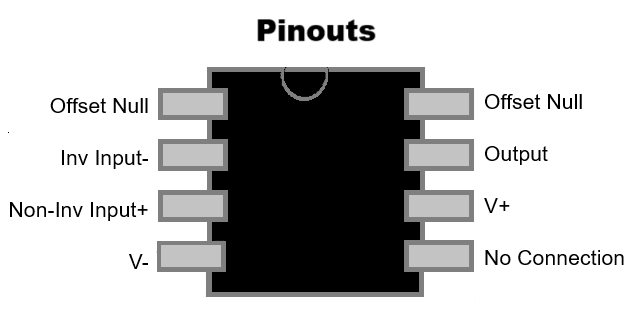
Pin Numbering on ICs - How to Identify Pins
Pin numbering on ICs (integrated circuits) follows a standardized layout, depending on the package type (e.g., DIP, SOIC, TSSOP). Here’s how to read them:
- Start at the top left (next to a notch or dot).
- Number goes counterclockwise around the chip.
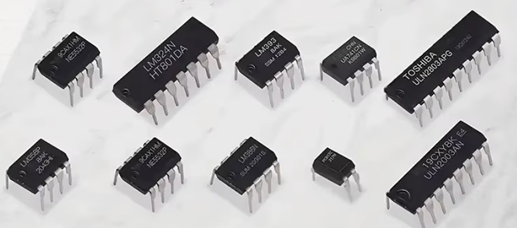
Here are some common Intergrated Circuits
 There are many types of standard ICs, each type serves a particular purpose. They most (but not all) have a similar general layout. At one end is a mark or indentation that indicated where the 'top' of the IC is, and the pins are numbered anticlockwise from that point. Where the indicator is not a central notch, it usuallu is closest to pin 1 of the IC. The type of IC, and sometimes (not always) the name of the manufacturer is printed on the IC.
There are many types of standard ICs, each type serves a particular purpose. They most (but not all) have a similar general layout. At one end is a mark or indentation that indicated where the 'top' of the IC is, and the pins are numbered anticlockwise from that point. Where the indicator is not a central notch, it usuallu is closest to pin 1 of the IC. The type of IC, and sometimes (not always) the name of the manufacturer is printed on the IC. ←Index
←Index